 Refractory Bricks Classification Based On Quality Standard
Refractory Bricks Classification Based On Quality StandardThere are many classifications of refractory materials. These include based on shape, properties, composition, and so on.
In this article, we will discuss the classification of refractory bricks based on quality standards.
The quality standards for refractory bricks refer to the standards issued by American Standard Testing and Materials or ASTM International.
So, what are the classifications based on ASTM International quality standards? Check out the explanation below!
Silica Brick (C 416-97 ASTM)
The composition of Silica Brick is as follows:
a) AI₂O₃ < 1.5 %
b) TiO₂ < 0.2 %
c) Fe₂O₃ < 2.5%
d) CaO < 4.0 %
The presence of contaminants in silica bricks tends to reduce refractoriness and their use is limited.
The amount of alkali and alumina can be used to estimate refractoriness properties.
Silica Bricks are classified based on impurities and usually called flux factor.
Alumina Silicate (fire clay) and high alumina bricks (C 27-98 ASTM)
Alumina-silica Refractory Bricks are produced from various combinations of alumina and silica grades.
The variation in chemical composition is quite wide, ranging from almost 100% alumina with a little silica, to almost 100% silica with a little alumina.
Classification based on chemical composition and physical properties consists of:
1. Fire clay bricks are classified based on physical properties, which can be an overlap between alumina and silica content:
Super-duty, High-duty, Semi-silica, Medium-duty, and Low-duty.
2. High alumina bricks are classified based on alumina content: 50, 60, 70, 80, 85, 90, and 99%.
Schamotte Insulating Brick (Insulating Fire Brick)
The classification of heat insulating materials is known as samot insulating brick (insulating fire brick). This insulating material is suitable for lining certain types of industrial furnaces.
AI₂O₃ - SiO₂ Insulation Brick (fire brick) ASTM C 155 - 97 is classified as follows:
|
Kelas |
Shrinkage max 2% on Temp°C |
Bulk Density max Lb/ft3 (g/cm3) |
|
16 |
845 |
0,54 |
|
20 |
1065 |
0,64 |
|
23 |
1230 |
0,77 |
|
26 |
1400 |
0,86 |
|
28 |
1510 |
0,96 |
|
30 |
1620 |
1,09 |
|
32 |
1730 |
1,52 |
|
33 |
1790 |
1,52 |
Call us and get your high quality fire bricks!
Phone: 0821-4280-8500
E-mail : info@lokarefractories.com
 Refractory Failure: Abrasion
Refractory Failure: AbrasionGenerally, abrasion is known as the process of coastal erosion due to pressure from sea waves.
Then, did you know that abrasion can also occur on refractory materials?
Refractory failure can occur due to abrasion so that it experiences erosion or wear due to mechanical work such as grinding, friction, rubbing, etc.
Each refractory material has a different abrasion resistance.
The abrasion resistance of refractory materials is influenced by the Modulus of Rupture, impact particle size and spray pressure, as well as impact angle and impact particle size.
Want to know more? Check out the explanation below!
Modulus of Rupture (MOR) is a measure of the strength of refractory material before it cracks and breaks. Abrasion resistance is inversely proportional to MOR. The higher the volume lost due to abrasion, the lower the MOR of the material.
The crusher particle size and spray pressure also affect abrasion resistance. The greater the size/mass and pressure, the greater the kinetic energy and the volume lost by abrasion increases.
Apart from that, the size of the impact particles and the impact angle have an influence on abrasion resistance which is explained as follows:
• The larger the size of the impact particle and the angle of collision, the greater the kinetic energy
• If the particle size of the crusher is smaller than the particle size of the aggregate, it will affect the matrix. Improve strength by decreasing matrix quantity.
• If the crusher particle size is smaller than the aggregate particle size, then choose aggregates with high abrasion resistance such as SiC and Al2O3.
Thus the article about refractory failure caused by abrasion. Get abrasion resistant refractory materials by contacting:
Phone: 0821-4280-8500
Website: www.lokarefractories.com
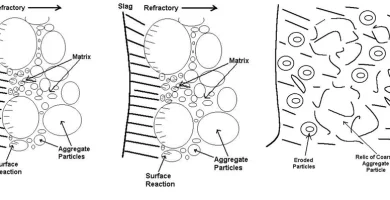 Corrosion : What It Is and How To Control It
Corrosion : What It Is and How To Control ItPreviously, our article is about refractory failure by spalling, which you can read here.
This time, we will discuss about corrosion which is the loss of mass of refractory material lining.
What caused it? How to prevent it? Scroll down and find out more!
What is corrosion?
Corrosion is the loss of refractory mass caused by chemical reactions between contacting materials.
Materials that come into contact with refractories can be solids, liquids or gases.
Corrosion can occur through four processes, namely dissolution, reaction, and penetration of chemical substances into the pores.
How to control corrosion process?
In general, the corrosion process can be prevented with the following steps:
- Reduces chemical reactivity and increases specific area. Because the finer the granules, the more reactive they are, so the substance dissolves more quickly into the melt.
- Set the composition of the filer and matrix.
- Reducing the dissolution rate by reducing the interface and melt concentration difference, avoiding stirring, and
lower the temperature.
- Regulate the suitability of the acidity level between the refractory and the slag.
- Controlling porosity and texture by:
1. Using wide range particle distribution to reduce interconnection between pores.
2. Improved mixing and molding techniques during production.
3. Adding ingredients that allow pore closure.
- Controling the penetration process with
increases viscosity and covers pores.
- Controlling dissolution by regulating chemical reactivity and specific area, and lowering temperature.
- Controlling oxidation - reduction reactions by adjusting the composition/addition of oxidation preventers.
That was a brief explanation about corrosion of refractory linings and how to control it.
Get the best refractory solutions for your industry now by contacting:
Telephone: 0821-4280-8500/031-7665507
E-mail: marketing@lokarefractories.com
 Refractory Failure: Spalling
Refractory Failure: SpallingRefractory materials installed in a furnace will be in contact with extreme environments such as high temperatures and high pressure. Therefore, refractory failure can happen if the right material is not used.
There are many types of refractory failure caused by various factors. One of the most common things that occurs is spalling. What is spalling and what causes it? Check out the explanation below!
What is Spalling?
Spalling is the release of part of the material from its parent due to internal pressure (stress) of the material in response to changes in environmental conditions. Usually, spalling starts from the appearance of cracks or splitting of the installed material.
There are three types of spalling with different causes, namely thermal spalling, structural spalling, and mechanical spalling.
Types of Spalling
Thermal spalling is material damage by temperature shock which results in temperature differences that cause stress.
Damage occurs through the formation of initial cracks due to stress caused by temperature shock which is greater than the strength of the material and is followed by crack propagation.
Structural Spalling is spalling caused by changes in phase (mineralogy, form), so that differences in the properties of the changed and original parts cause internal stress.
Structural spalling is caused by overheating and chemical reactions/penetration.
Structural spalling caused by overheating can be prevented by:
- Temperature control
- Control of intake air or furnace atmosphere
- Selection of appropriate refractory
Meanwhile, those caused by chemical reactions and penetration are prevented by:
- Selection of refractory materials according to the nature of the environment in the furnace (acid, neutral, alkaline)
- Arrangement of porosity, pore size distribution, wettability, etc.
Mechanical Spalling is a failure that is often caused by concentrated loads due to unequal distribution of mechanical forces.
One of them is the lining design on the refractory and metal connections such as steel anchors, and on the masonry in the furnace arc. Another cause is the use of inappropriate materials.
Spalling or other refractory failures can be prevented by selecting refractory materials with the right specifications and good quality.
Get the best quality refractory materials from Loka Refractories! Contact us for our best offer!
Phone : 0821-4280-8500
E-mail: marketing@lokarefractories.com
Image source :
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11661-011-0635-x/figures/13
 Fire Clay Bricks and Regular Clay Bricks, What's the Difference?
Fire Clay Bricks and Regular Clay Bricks, What's the Difference?In terms of appearance, both of them look similar. But actually, they are very different!
Fire clay bricks and regular clay bricks have very different uses and compositions. The differences will be outlined in the following explanation.
Differences between fire clay bricks and regular clay bricks
First, let's discuss the difference in composition.
Fire clay bricks have a main composition of alumina derived from bauxite and silica derived from quartz sand.
These raw materials have refractory properties that make them resistant to very high temperatures.
In addition to alumina and silica, refractory bricks also have other raw materials such as magnesia, carbon, silica carbide, and so on according to their needs and applications.
Meanwhile, regular clay bricks are made from clay with additives such as sand, lime, ash, and so on. Therefore, they do not have refractory properties.
Second, let's compare their uses. Regular clay bricks are commonly used to build walls of houses, buildings, and many more.
Whereas fire clay bricks are used to build lining in furnaces, ovens, boilers, ladles, reformers that involve heat energy and high pressure.
The thing is, regular clay bricks are resistant to fire. However, it does not have resistance to temperatures up to 1800 C as well as pressure and abrasion.
Another difference is that regular clay brick has a much cheaper price than fire clay bricks.
If you need clay bricks, you can find them easily at the nearest building store.
Finding refractory bricks is no less easy. Contact Loka Refractories at:
Phone : (031) 7663307/0821-4280-8500
E-mail : info@lokarefractories.com
We supply refractory bricks with standard sizes (230x114x65mm) and custom sizes according to your industry needs!
 Refractory Material Resistance Test
Refractory Material Resistance TestLoka Refractories - In addition to high temperature and pressure resistance, refractory materials must also be resistant to abrasion.
Abrasion itself is damage in the form of erosion of the refractory lining due to friction with the material in the kiln/furnace/boiler.
Refractory damage can hinder industrial processes and cause considerable losses.
Therefore, refractory materials must be tested for abrasion resistance. One of the indicators is Cold Crushing Strength (CCS) or compressive strength.
What is cold crushing strength and how is it tested? Check out the article below!
- What is Cold Crushing Strength?
Cold Crushing Strength or also known as compressive strength is the ability to withstand refractory materials against compression loads at room temperature.
From the CCS test, information is obtained on the strength in transportation, combustion suitability and resistance to abrasion, bulk density and porosity.
There are many standards for conducting CCS tests, one of which is ASTM C133.
- How is the CCS Test Performed?
The CCS test is conducted by placing a molded or mortar refractory stone or refractory cement sample on a special machine.
Then, the sample will be loaded until it reaches the maximum load and cracks (hydraulic compression). The maximum load will be used to calculate the CCS value.
Cold Crushing Strength is also an indicator of abrasion resistance for PT Loka Refractories products.
Get materials that are tested for performance and quality by contacting:
E-mail : info@lokarefractories.com
Phone : 031-7663307, 0821-4280-8500


